Why Enterprises Are Moving Workloads Back to On-Premise Private Cloud for Next-Gen AI

There has been a clear trend in enterprise IT strategies in recent years, as firms are progressively moving workloads from the public cloud back to on-premise private clouds. The phenomenon known as “cloud repatriation” is particularly noticeable when it comes to advanced workloads such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). In these cases, ensuring data privacy, security, and control is of utmost importance. This blog article will analyse the factors behind this change and provide illustrations of businesses that have transitioned accordingly.
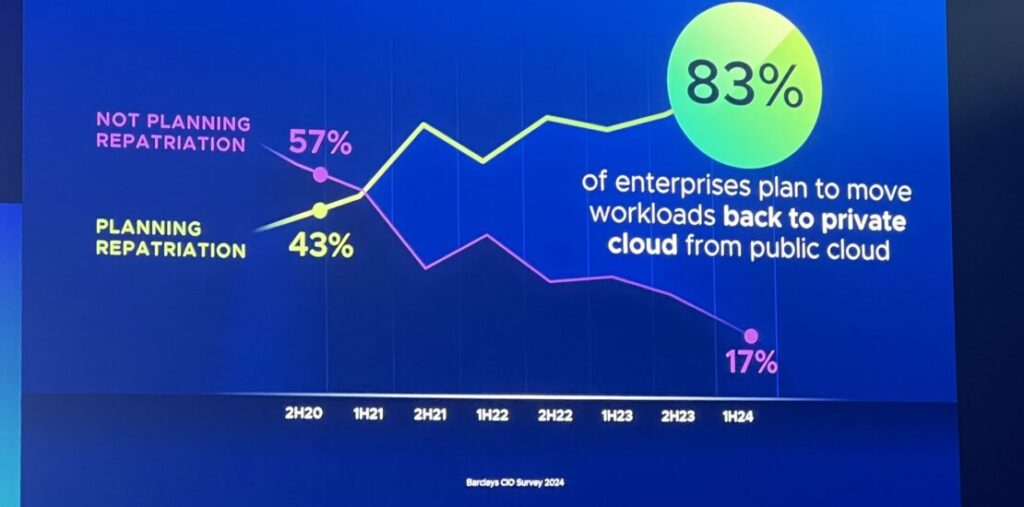
The Evolution of Cloud Adoption
Public cloud systems such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have transformed enterprise IT by providing scalable and readily available resources. Businesses eagerly adopted these platforms in order to decrease expenses related to infrastructure, enhance flexibility, and expedite the development of new ideas. Nevertheless, as workloads grew more intricate and data-heavy, particularly with the integration of artificial intelligence, the drawbacks of relying only on the public cloud became increasingly apparent.
Why Repatriation for AI Workloads?
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns
AI and ML applications heavily rely on extensive datasets, a significant portion of which consists of sensitive and confidential information. Due to the implementation of strict data protection requirements like GDPR and CCPA, organisations are becoming more vigilant regarding the storage and processing of their data. On-premise private clouds provide enterprises with greater control over data security and compliance, allowing them to safeguard critical information from external threats and unauthorised access. - Cost Efficiency
Although public cloud platforms were first perceived as cost-effective, numerous organisations are discovering that the costs linked to operating extensive AI workloads can rapidly climb. The expenses associated with data egress fees, storage costs, and the requirement for continuous growth might render the use of public cloud services excessively costly. On-premise private clouds, albeit necessitating a greater upfront expenditure, offer the advantage of more reliable and potentially reduced expenses over the long run, particularly for businesses with consistent and continuous AI workloads. - Performance and Latency
AI tasks, especially those that involve processing data in real-time, require computing resources that have high performance and low latency. On-premise environments can be fine-tuned to cater to these specific requirements, resulting in decreased latency and enhanced overall performance. However, the fact that public clouds are designed to accommodate several tenants can lead to latency problems that may be deemed undesirable for specific AI applications. - Regulatory Compliance
Certain sectors are subject to restrictions that require specified categories of data to be stored within a designated geographic area or under the direct control of the company. On-premise private clouds offer the essential amount of control to comply with these legal standards, a feat that is often challenging to do in the public cloud.
Examples of Cloud Repatriation for AI Workloads
Several high-profile companies have already begun the process of moving their AI workloads back to on-premise private clouds:
- Dropbox
Dropbox originally functioned exclusively in the public cloud but gained significant attention in 2016 when it announced a substantial migration to a private cloud infrastructure. Dropbox achieved cost savings of approximately $75 million over a period of two years by internalising its workloads and customising its hardware and software to meet its own requirements. Although not explicitly aimed at AI, this action emphasises the possible financial advantages and managerial control that businesses might attain by bringing operations back to their home country. Dropbox Success Story - Apple
Apple has established a reputation for prioritising privacy and exerting control. The corporation has been progressively transferring its workloads, notably those associated with artificial intelligence, from the public cloud to its proprietary data centres. Apple maintains the security and control of sensitive data, specifically user data, by keeping AI workloads on-premise, in accordance with its privacy obligations. Apple and AI Workloads - Target
Target is a corporation that has transitioned from using the public cloud for specific workloads. The retailer relocated its e-commerce and data operations, which include AI-driven analytics, back to its private data centres. The decision to make this change was motivated by the necessity to manage expenses, enhance efficiency, and guarantee the confidentiality of data, all of which are crucial elements in the fiercely competitive retail sector. Target’s Cloud Journey
Conclusion
Enterprises are increasingly adopting cloud repatriation to achieve a balance between the flexibility offered by the public cloud and the control provided by on-premise settings. The advantages of improved security, cost effectiveness, and performance make private cloud a compelling choice for next-generation applications such as AI. Although the public cloud will remain important in enterprise IT, the choice to bring back some workloads underscores the changing priorities of organisations as they deal with the complexity of modern data management.
Enterprises can choose the most appropriate environment for their AI and ML applications by thoroughly evaluating their workloads and infrastructure requirements. This evaluation ensures that the apps are not only innovative but also meet security and compliance standards.
The increasing adoption of on-premise private clouds for AI workloads is a noteworthy development that has the potential to change the cloud industry in the future. For businesses, the choice is not solely focused on technology; it involves guaranteeing the security, privacy, and ownership of their most important resource—data.
